Wait for User Input
utility to render graph respresentation in PlantUML
import net.sourceforge.plantuml.SourceStringReader;
import net.sourceforge.plantuml.FileFormatOption;
import net.sourceforge.plantuml.FileFormat;
import org.bsc.langgraph4j.GraphRepresentation;
void displayDiagram( GraphRepresentation representation ) throws IOException {
var reader = new SourceStringReader(representation.getContent());
try(var imageOutStream = new java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream()) {
var description = reader.outputImage( imageOutStream, 0, new FileFormatOption(FileFormat.PNG));
var imageInStream = new java.io.ByteArrayInputStream( imageOutStream.toByteArray() );
var image = javax.imageio.ImageIO.read( imageInStream );
display( image );
}
}
Define graph with interruption
import org.bsc.langgraph4j.*;
import org.bsc.langgraph4j.prebuilt.MessagesState;
import org.bsc.langgraph4j.state.Channel;
import dev.langchain4j.data.message.AiMessage;
import dev.langchain4j.data.message.ChatMessage;
import org.bsc.langgraph4j.action.AsyncNodeAction;
import org.bsc.langgraph4j.action.AsyncEdgeAction;
import static org.bsc.langgraph4j.action.AsyncNodeAction.node_async;
import static org.bsc.langgraph4j.action.AsyncEdgeAction.edge_async;
import org.bsc.langgraph4j.checkpoint.MemorySaver;
import org.bsc.langgraph4j.CompileConfig;
import static org.bsc.langgraph4j.StateGraph.END;
import static org.bsc.langgraph4j.StateGraph.START;
public class State extends MessagesState<String> {
public State(Map<String, Object> initData) {
super( initData );
}
public Optional<String> humanFeedback() {
return value("human_feedback");
}
}
AsyncNodeAction<State> step1 = node_async( state -> {
return Map.of( "messages", "Step 1" );
});
AsyncNodeAction<State> humanFeedback = node_async( state -> {
return Map.of();
});
AsyncNodeAction<State> step3 = node_async( state -> {
return Map.of( "messages", "Step 3" );
});
AsyncEdgeAction<State> evalHumanFeedback = edge_async( state -> {
var feedback = state.humanFeedback().orElseThrow();
return ( feedback.equals("next") || feedback.equals("back") ) ? feedback : "unknown";
});
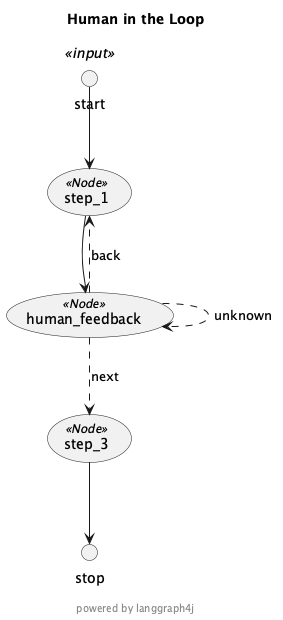
var builder = new StateGraph<>(State.SCHEMA, State::new)
.addNode("step_1", step1)
.addNode("human_feedback", humanFeedback)
.addNode("step_3", step3)
.addEdge(START, "step_1")
.addEdge("step_1", "human_feedback")
.addConditionalEdges("human_feedback", evalHumanFeedback,
Map.of( "back", "step_1", "next", "step_3", "unknown", "human_feedback" ))
.addEdge("step_3", END)
;
// Set up memory
var saver = new MemorySaver();
// Add
var compileConfig = CompileConfig.builder()
.checkpointSaver(saver)
.interruptBefore("human_feedback")
.releaseThread(true)
.build();
var graph = builder.compile(compileConfig);
displayDiagram( graph.getGraph(GraphRepresentation.Type.PLANTUML, "Human in the Loop", false) );
SLF4J: No SLF4J providers were found.
SLF4J: Defaulting to no-operation (NOP) logger implementation
SLF4J: See https://www.slf4j.org/codes.html#noProviders for further details.
Start graph until interruption
// Input
Map<String,Object> initialInput = Map.of("messages", "Step 0");
// Thread
var invokeConfig = RunnableConfig.builder()
.threadId("Thread1")
.build();
// Run the graph until the first interruption
for (var event : graph.stream(initialInput, invokeConfig)) {
System.out.println(event);
}
NodeOutput{node=__START__, state={messages=[Step 0]}}
NodeOutput{node=step_1, state={messages=[Step 0, Step 1]}}
Wait for user input and update state
⚠️ The Java notebook, until now, doesn't support user input (take a look issue #39) so we could simulate input ⚠️
// We can check the state
System.out.printf("--State before update--\n%s\n", graph.getState(invokeConfig));
// Simulate user input
var userInput = "back"; // back means we want to go back to the previous node
System.out.printf("\n--User Input--\nTell me how you want to update the state: '%s'\n\n", userInput);
// We now update the state as if we are the human_feedback node
var updateConfig = graph.updateState(invokeConfig, Map.of("human_feedback", userInput), null);
// We can check the state
System.out.printf("--State after update--\n%s\n", graph.getState(invokeConfig) );
// We can check the next node, showing that it is node 3 (which follows human_feedback)
System.out.printf("\ngetNext()\n\twith invokeConfig:[%s]\n\twith updateConfig:[%s]\n",
graph.getState(invokeConfig).getNext(),
graph.getState(updateConfig).getNext());
;
--State before update--
StateSnapshot{node=step_1, state={messages=[Step 0, Step 1]}, config=RunnableConfig{ threadId=Thread1, checkPointId=98923510-ce29-4a73-a997-f1b4a8ea8c0e, nextNode=human_feedback, streamMode=VALUES }}
--User Input--
Tell me how you want to update the state: 'back'
--State after update--
StateSnapshot{node=step_1, state={messages=[Step 0, Step 1], human_feedback=back}, config=RunnableConfig{ threadId=Thread1, checkPointId=98923510-ce29-4a73-a997-f1b4a8ea8c0e, nextNode=human_feedback, streamMode=VALUES }}
getNext()
with invokeConfig:[human_feedback]
with updateConfig:[human_feedback]
Continue graph execution after interruption
// Continue the graph execution
for (var event : graph.stream(null, updateConfig)) {
System.out.println(event);
}
NodeOutput{node=human_feedback, state={messages=[Step 0, Step 1], human_feedback=back}}
NodeOutput{node=step_1, state={messages=[Step 0, Step 1], human_feedback=back}}
Waif for user input (again) and update state
⚠️ The Java notebook, until now, doesn't support user input (take a look issue #39) so we could simulate input ⚠️
var userInput = "next"; // 'next' means we want to go to the next node
System.out.printf("\n--User Input--\nTell me how you want to update the state: '%s'\n", userInput);
// We now update the state as if we are the human_feedback node
var updateConfig = graph.updateState(invokeConfig, Map.of("human_feedback", userInput), null);
System.out.printf("\ngetNext()\n\twith invokeConfig:[%s]\n\twith updateConfig:[%s]\n",
graph.getState(invokeConfig).getNext(),
graph.getState(updateConfig).getNext());
;
--User Input--
Tell me how you want to update the state: 'next'
getNext()
with invokeConfig:[human_feedback]
with updateConfig:[human_feedback]
Continue graph execution after the 2nd interruption
// Continue the graph execution
for (var event : graph.stream(null, updateConfig)) {
System.out.println(event);
}
NodeOutput{node=human_feedback, state={messages=[Step 0, Step 1], human_feedback=next}}
NodeOutput{node=step_3, state={messages=[Step 0, Step 1, Step 3], human_feedback=next}}
NodeOutput{node=__END__, state={messages=[Step 0, Step 1, Step 3], human_feedback=next}}

