LangGraph4j Meets AG-UI - Building UI/UX in AI Agents era

AI Agents ecosystem evolution
The rapid evolution of artificial intelligence has brought a new wave of innovation: the rise of AI agents. These agents—autonomous, intelligent, and capable of interacting with users and services—are changing how we build applications, automate workflows, and even communicate online. However, as this ecosystem expands, a new challenge has emerged: interoperability. How can these agents reliably talk to each other, work with external tools, and offer seamless experiences to human users?
This challenge has led to the development of new standards—protocols that define how AI agents communicate with the world and each other. Among the most notable are:
- MCP (Agent-to-Tools)
Standardizing Agent to Tools/Services Communication
- A2A (Agent-to-Agent Protocol)
Standardizing Agent to Agent Communication
- AG-UI (Agent-to-User)
Standardizing Agent to User Communication
In this article we will focus on AG-UI protocol an how it helps us to develop an effective User eXperience in using AI Agents
What is AG-UI protocol ?
AG-UI bridges the gap between AI agents and their human users, ensuring that interactions are intuitive, consistent, and user-friendly. It defines the structure for how agents present information, take user input, and handle conversations—regardless of the underlying platform or application.
Why AG-UI Compliance Matters
By aligning with AG-UI, LangGraph4j agents can present rich, interactive interfaces to user, whether embedded in web apps, desktop tools, or chatbots. This standardization means that developers can focus on building great agent logic, while relying on AG-UI to handle the complexities of user interaction.
LangGraph4j and AG-UI
LangGraph4j is a Java-based framework designed for building and orchestrating AI agent workflows. It is already capable to use MCP servers inside workflow steps and has also experimented integration with A2A (see here).
Copilotkit integration
With its latest project, langgraph4j-copilotkit, we have evaluated how to make LangGraph4j compliant with the AG-UI protocol, integrating CopilotKit that is its reference implementation for help and enhance developer experience in building better either User Interfaces (UI) and User eXperience (UX).
Architecture
The architecture of the langgraph4j-copilotkit integration is designed to enable seamless communication between a user-facing frontend and the LangGraph4j backend. Here’s a breakdown of the key components and their interactions:
The following diagram illustrates a diagram that shows the sequence of messages exchanged between main actors of the architecture:
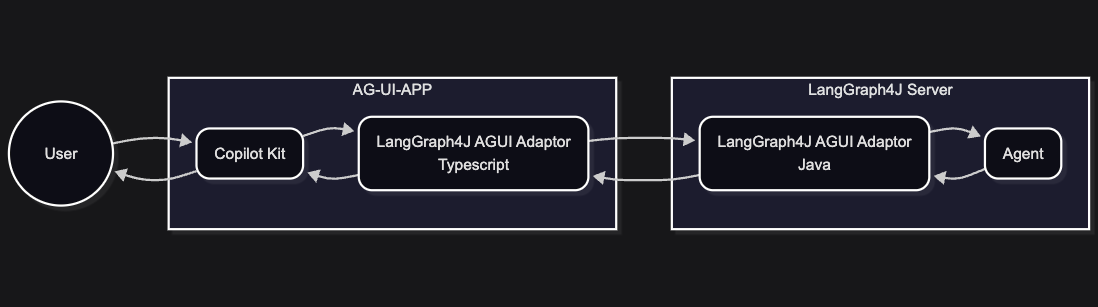
Explanation of the diagram:
-
User & Frontend (CopilotKit): The user interacts with a web application that has the CopilotKit SDK integrated. CopilotKit handles the UI rendering and state management, translating user actions into requests compliant with the AG-UI protocol.
-
Backend (langgraph4j-copilotkit): A backend server, built with a framework like Spring Boot, includes the langgraph4j-copilotkit library. This library exposes an endpoint that listens for AG-UI requests from the frontend. It acts as a bridge, translating incoming requests into executable commands for the LangGraph4j agent, and in turn translates the agent’s responses into compatible AG-UI events.
The communication is typically asynchronous and streaming. As the LangGraph4j agent produces results or requires further input, langgraph4j-copilotkit streams these events back to the frontend in the AG-UI format. CopilotKit then dynamically updates the UI, creating a responsive and interactive user experience.
This architecture decouples the frontend presentation layer from the backend agentic logic, allowing developers to build sophisticated AI agents with LangGraph4j while providing a rich, standardized user interface with CopilotKit.
Example - Approval action (Human-in-the-Loop)
This example demonstrates how to implement a “Human-in-the-Loop” (HITL) approval action using langgraph4j-copilotkit. The user will be asked to approve an action (sendEmail) before it is executed.
Frontend
The frontend uses @copilotkit/react-core and @copilotkit/react-ui to create the chat interface and handle the approval action. The useCopilotAction hook is used to define the sendEmail action. When the action is triggered, it renders a confirmation dialog asking the user for approval.
chatApproval.tsx
"use client";
import { useCopilotAction } from "@copilotkit/react-core";
import { CopilotChat } from "@copilotkit/react-ui";
export function SimpleChatWithApproval() {
useCopilotAction( {
name: "sendEmail",
description: "Sends an email after user approval.",
parameters: [
{ name: "address", type: "string" },
{ name: "subject", type: "string" },
{ name: "body", type: "string" },
],
renderAndWaitForResponse: ({ args, status, respond }) => {
console.debug( "renderAndWaitForResponse", respond, status, args );
if (status === "inProgress") {
return (
<div>
<h2>Sending Email</h2>
<p>Preparing to send email...</p>
</div>
);
}
if (status === "executing") {
return (
<div>
<h2>Confirm Email</h2>
<p>Send email to <b>{args.address}</b> with subject "<b>{args.subject}</b>"?</p>
<p><i>{args.body}</i></p>
<div>
<button onClick={() => respond?.('APPROVED')}>
Approve
</button>
<button onClick={() => respond?.('REJECTED')}>
Cancel
</button>
</div>
</div>
);
}
return <></>
}});
return (
<CopilotChat
instructions={"You are assisting the user as best as you can. Answer in the best way possible given the data you have."}
labels=
className="w-full"
/>
);
}
LangGraph4j Agent
The backend is a LangGraph4j agent that defines the sendEmail tool. The AgentExecutorEx is configured to require approval for the sendEmail tool. When the tool is about to be executed, the agent will be interrupted, and an approval request will be sent to the frontend.
AGUIAgentExecutor.java:
public class AGUIAgentExecutor extends AGUILangGraphAgent {
// define tools
public static class Tools {
@Tool( description = "Send an email to someone")
public String sendEmail(
@ToolParam( description = "destination address") String to,
@ToolParam( description = "subject of the email") String subject,
@ToolParam( description = "body of the email") String body
) {
// This is a placeholder for the actual implementation
return format("mail sent to %s with subject %s", to, subject);
}
}
@Override
GraphData buildStateGraph() throws GraphStateException {
// Create agent
var agent = AgentExecutorEx.builder()
.chatModel(LLM, true)
.toolsFromObject(new Tools())
.approvalOn( "sendEmail",
(nodeId, state ) ->
InterruptionMetadata.builder( nodeId, state )
.build()
)
.build();
return new GraphData( agent ) ;
}
// invoked on interruption to provide approval information back to the client
@Override
<State extends AgentState> List<Approval> onInterruption(AGUIType.RunAgentInput input, InterruptionMetadata<State> metadata ) {
var messages = metadata.state().value("messages");
.orElseThrow( () -> new IllegalStateException("messages not found into given state"));
return lastOf(messages)
.flatMap(MessageUtil::asAssistantMessage)
.filter(AssistantMessage::hasToolCalls)
.map(AssistantMessage::getToolCalls)
.map( toolCalls ->
toolCalls.stream().map( toolCall -> {
var id = toolCall.id().isBlank() ?
UUID.randomUUID().toString() :
toolCall.id();
return new Approval( id, toolCall.name(), toolCall.arguments() );
}).toList()
)
.orElseGet(List::of);
}
}
This setup allows for a seamless HITL workflow where the user has the final say on critical actions, all orchestrated through the AG-UI protocol and the langgraph4j-copilotkit integration.
Demo

Conclusion
We can state that the future of AI development will be to have a Unified AI Agent Ecosystem. The convergence of these standards like MCP, A2A, and AG-UI is a step toward this vision.
We consider crucial keep working to improve support of them in LangGraph4j to provide a complete infrastructure for AI Agents to communicate with tools, collaborate with each other, and engage users in a standardized and interoperable manner.
As more frameworks and tools adopt these protocols, we can expect to see a new generation of AI-powered applications that are more flexible, extensible and, with AG-UI, more user-centric than ever before.
Hope this could help your AI Java developing journey, in the meanwhile happy AI coding! 👋