Enhance your CLI with AI (Part 1)
Potential of AI
Imagine having an AI-powered Command Line Interface (CLI) that can enhance your productivity and make your life easier. With the power of Large Language Model (LLM) models like GPT 3.5/4, you can simply ask for the right command line for any task, and the AI will provide the appropriate commands for your operating system.
For example, you could ask the AI, ‘What is the command to list files in a folder?” and it will instantly give you the correct command, be it ‘ls’ for Linux or ‘dir’ for Windows.
The only challenge here is to execute the given command into target environment
OpenAI function Calling
This idea revolves around leveraging the capabilities of OpenAI and its powerful function calling features. By integrating AI into the CLI, you can streamline your workflow and save time and effort by quickly obtaining the right commands without extensive manual searching or trial-and-error.
But we can do more, we can add custom commands that further extends your CLI enabling the possibility to create very complex workflow in easy way especially because we use the natural language processing to achieve this
The proposed solution
Solution has been based on Langchain Framework (in particular the JS/TS release) and OpenAI Functions Agent.
Why langchain ?
Langchain is a powerful framework for building applications that leverage language models. It offers standardized components and abstractions, making it easier to develop apps that are data-aware and capable of interacting with their environment. By using Langchain, you can tap into the capabilities of language models like GPT 3.5/4 and enable your CLI to understand and process natural language input.
OpenAI function Agent
One of the key concepts in Langchain is the Agent. The Agent acts as a crucial component with access to a range of tools and functionalities. It is responsible for making decisions based on the user’s input and utilizing the appropriate tools within the application. In particular OpenAI function Agent utilizes GPT 3/4’s ability to comprehend required function calls, producing necessary inputs.
Let’s create an langchain Agent able to recognize and execute generic system commands
The combination of Langchain and ReACT allows you to create specialized tools for each command you want to integrate into your CLI. These tools are designed to understand natural language input, process it, and generate appropriate responses based on the context of the conversation. This integration enables your CLI to handle complex workflows, understand user request, and provide accurate and helpful responses in a conversational manner.
The following Javascript code use the Langchain.js framework and the OpenAI Functions Agent.
const model = new ChatOpenAI({ modelName: "gpt-3.5-turbo-0613", temperature: 0});
const tools = [ new SystemCommandTool() ];
const agent = await initializeAgentExecutorWithOptions(tools, model,
{ agentType: "openai-functions" } );
We started by creating a new instance of the ChatOpenAI class, initializing it with specific options like the model name, and temperature.
After that, we created an array of tools, including a SystemCommandTool instance responsible to execute every recognised system command
class SystemCommandTool extends Tool {
name ="system_cmd"
description = "all system commands" // description instruct LLM on Tool's purpose
protected async _call(arg: any): Promise<string> {
console.debug( "System Command:", arg)
const code = await runCommand( arg ) // exec command in target environment
return `command executed: ${code ?? ''}`
}
}
Finally, we initialized an agent using the initializeAgentExecutorWithOptions function. We passed in the tools array, the model, and agent type that define its behaviour in our case openai-functions.
With this code, we set up a Langchain agent giving him the skill to be able to execute system command
Let’s create a prompt for instruct the AI what is its role and what are the rules that it must follow
Now we have to deals with the prompt template. The prompt template is a paramized structured text that provides context and guidance to the AI model. It helps set the expectations for the desired output and guides the model’s response.
const promptTemplate = PromptTemplate.fromTemplate(`
You are my command line executor assistant.
Limit your response to the word 'completed' and assume that we are on {platform} operative system:
{input}`
);
const prompt = await promptTemplate.format({
platform: os.platform(),
input: input
})
In this code, we define a promptTemplate that includes a placeholder for the {platform} and {input} values. The template itself suggests that the AI should answer always with “complete” word and also assuming that we are on a specific operating system based on the {platform} placeholder.
Such placeholders will be substitute with the current execution platform (os.platform()) and the user’s input.
let’s run the agent
After formatting the promptTemplate, we pass the result to the agent.run() function to execute the agent with the generated prompt. It sends the prompt to the Langchain agent, which uses the specified model and tools to generate a response based on the given context.
Finally, we log the result to the console, which represents the AI-generated response to the provided prompt.
const result = await agent.run( prompt );
console.log(result);
Examples
I created a freah new Git repository on GitHub copilot-cli-agent as a proof of concept. Here are some results of running the repository.
Request
List files in downloads folder?
Response
System Command: ls ~/Downloads
AppleDeveloper
Comics
Media
Personal
Xcode-beta.app
bartololabs_bak
timr45w.ttf
Request
List files in download folder with their size in Kb
Response
System Command: ls -lh ~/Downloads
drwxr-xr-x 7 bsorrentino staff 224B May 9 2022 AppleDeveloper
drwxr-xr-x 6 bsorrentino staff 192B Nov 6 2022 Comics
drwxr-xr-x@ 3 bsorrentino staff 96B Sep 5 16:41 Media
drwxr-xr-x 13 bsorrentino staff 416B Aug 4 09:56 Personal
drwxr-xr-x@ 3 bsorrentino staff 96B Aug 5 07:25 Xcode-beta.app
drwxr-xr-x@ 17 bsorrentino wheel 544B Aug 19 18:15 bartololabs_bak
-rw-r--r--@ 1 bsorrentino staff 94K Mar 4 2022 timr45w.ttf
Request
find Xcode app and ignoring error
Response
System Command: find /Applications -name Xcode.app 2>/dev/null
/Applications/Xcode.app
Debug, Test, Evaluate and Monitor Langchain’s calls
Part of LangChain suite and seamlessly integrated with it there is LangSmith platform that enable building production-grade LLM applications providing a way to debug, test, evaluate, and monitor chains and intelligent agents built on any LLM framework.
Let’s see the LangSmith output tracing request:
List files in download folder with their size in Kb
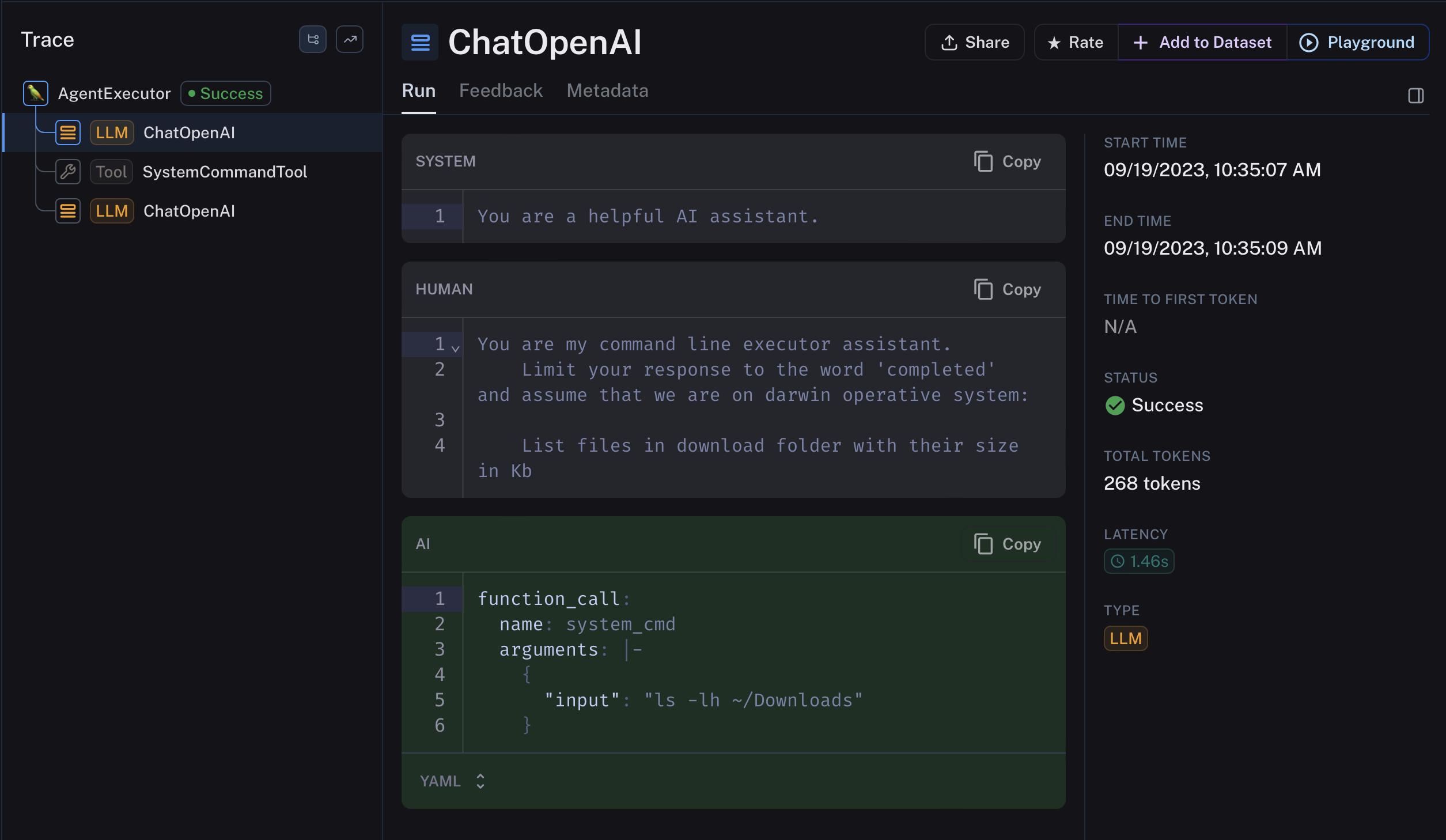
As we can see the Chain perform a first call to LLM model that evaluate prompt, recognize a command and translate it into a command shell for proper operative system, after that delegate execution to SysteCommandTool and after such execution involve again the LLM model to evaluate result and, if there aren’t further tasks to do, return result (i.e. complete).
Conclusion
Alrighty! 🚀 So, we’ve started to see the what happens when you use a bit of AI magic on your CLI. No more digging deep in memory or Googling to find that one command! 🧐 With the might of LLM models like GPT 3.5/4, you’ve got your very own command-line sidekick. 🦸 But is not finished here, We’ve just scratched the surface in this article, in Part 2, we’re gonna dive deeper and explore how to add your own custom command line commands invocable using natural language request. Imagine building your very own CLI shortcuts and commands that make your workflow smoother. So, stay tuned, and let’s keep leveling up that CLI game together. Catch you in the next one! ✌️😄